Submitted by WA Contents
Herzog & de Meuron designs raw interior for a flagship store with a network of beams and columns
Japan Architecture News - Jun 22, 2020 - 11:39 8044 views
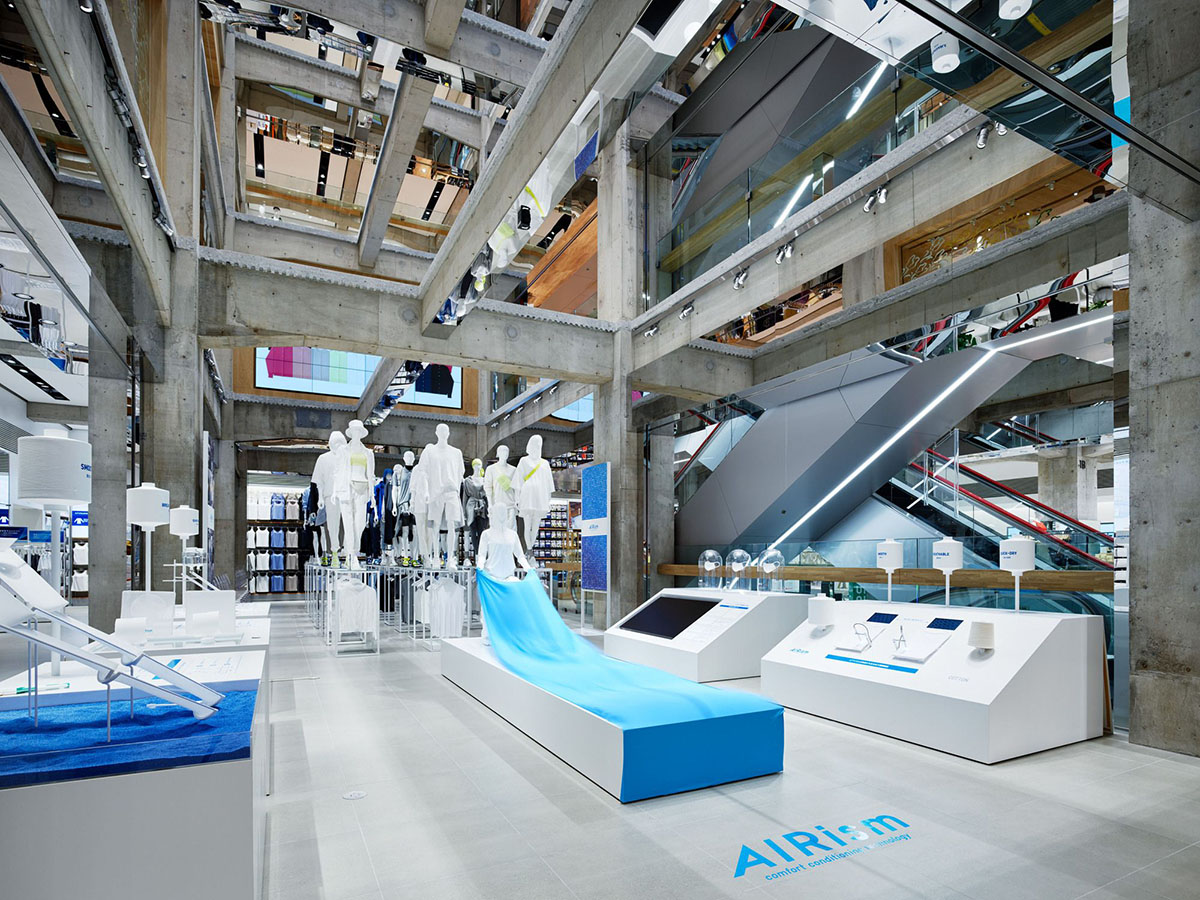

In this flagship store, visitors can see each other in every point of the store thanks to the open network of beams and columns that span the building.
Swiss firm Herzog & de Meuron has completed a flagship store in Tokyo for Uniqlo, a clothing apparel company, which was originally founded in Yamaguchi, Japan in 1949 as a textiles manufacturer.
Designed as a new flagship store of the company, Herzog & de Meuron followed a different design approach for this store, which helps visitors to see the showcased products and being seen from every levels.
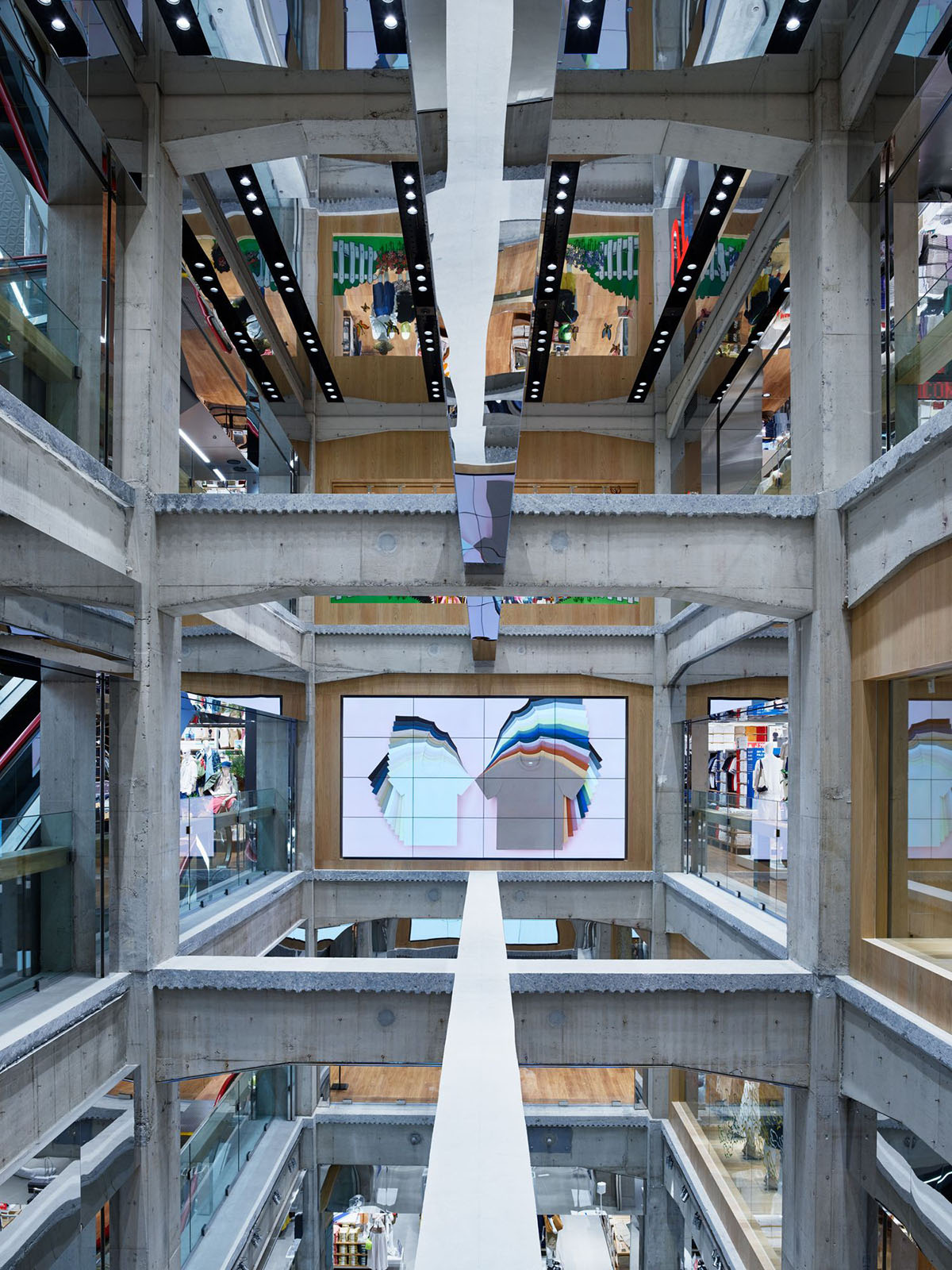

Called Uniqlo Tokyo Flagship Store, the 11-storey building was designed as open as possible.
In 2019 Uniqlo approached Herzog & de Meuron to reinvigorate an existing department store building in Ginza as a new global flagship store named Uniqlo Tokyo: a store showing the full range of Uniqlo's "LifeWear" and embodying the philosophy of high-quality, functionality, affordability, innovation and enjoyment for everybody.
The firm continued its design process through subtraction, and the architects stripped away the conventional retail interior to reveal the functionality and simplicity of the building's original concrete skeleton.
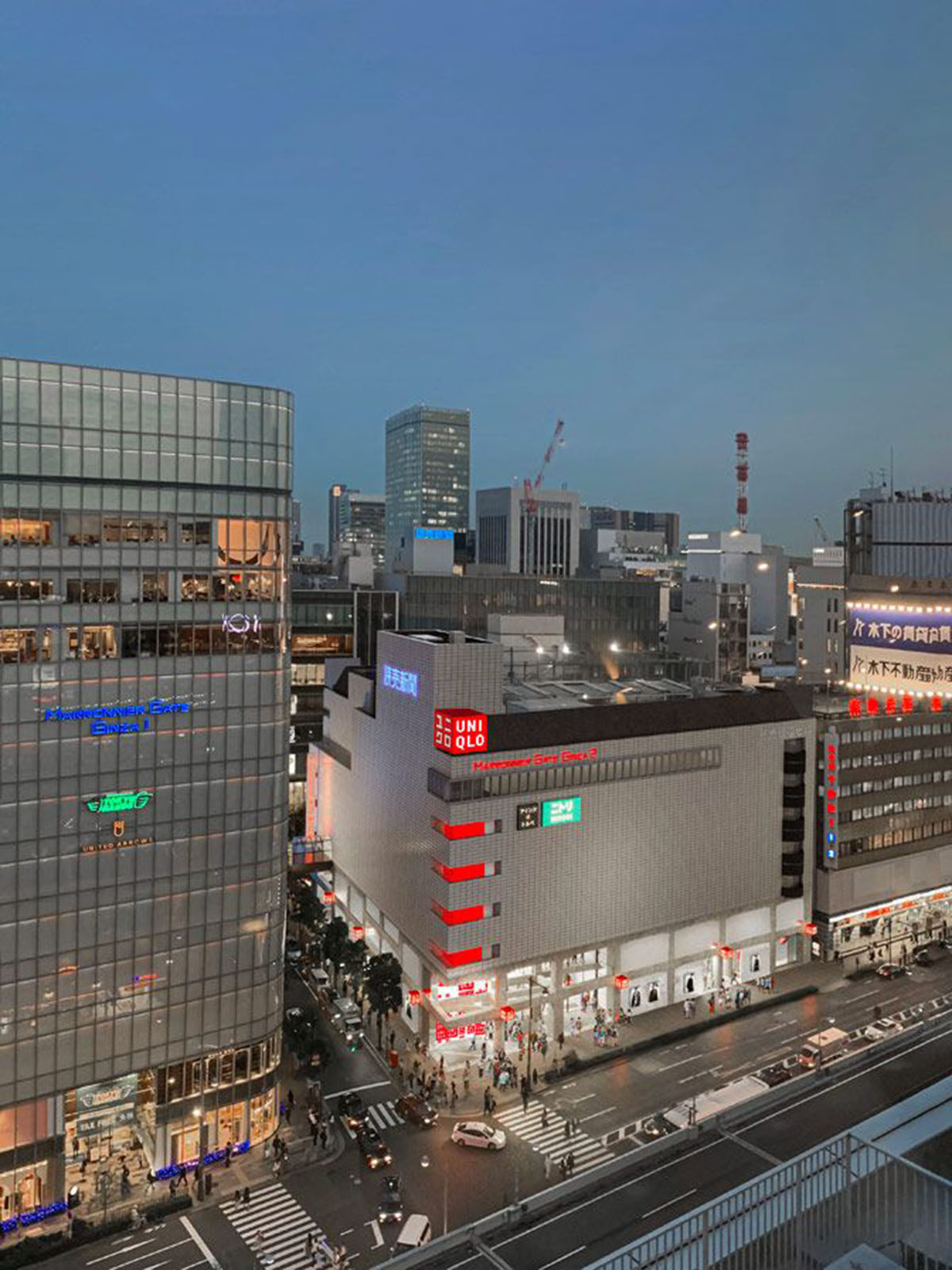

The architects aimed to showcase the brand's products as a whole by creating a raw but muted framework via a network of beams and columns.
"Double-height entrances and the interior quadruple-story plaza create remarkable views from all levels and a meeting point for people," said Herzog & de Meuron.
"Visitors see and are seen: everything at once. The vitality and voyeurism of Ginza street life extends into the heart of Uniqlo Tokyo."

Herzog & de Meuron explained their design approach below. The existing building Marronnier Gate is located at the edge of the dense urban fabric of Ginza, a district in the center of Tokyo with a high concentration of luxury stores.
In contrast, adjacent to the site is the open expanse of a wide avenue and elevated roadway. Thus, there are two perceptions of the building – tight, fragmentary glimpses from Ginza, and broad vistas from the roads and trainlines to nearby Tokyo Station. In both cases the exterior is perceived as a closed volume, revealing little of its content.
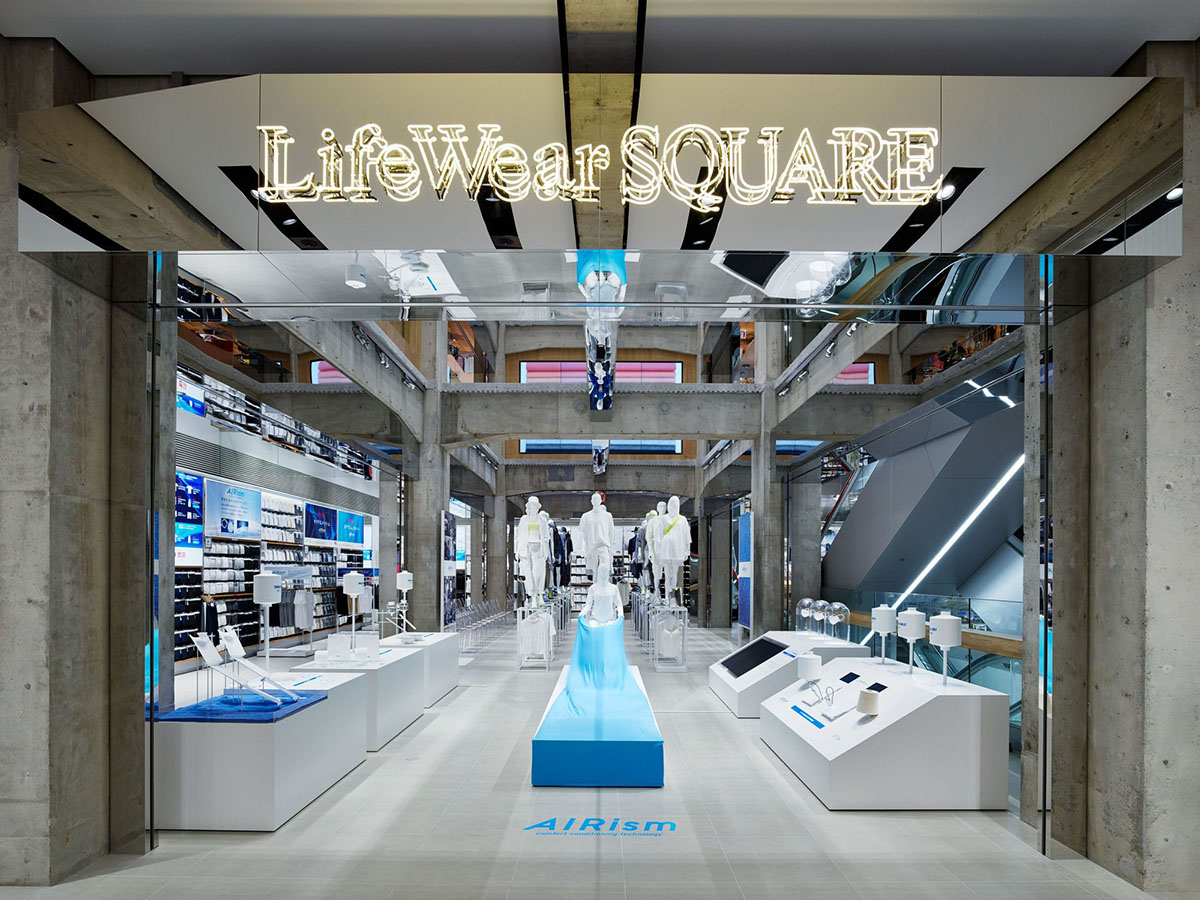

Marronnier Gate was built in 1984 to house the first large-scale Parisian-style department store in Tokyo. The building was designed to provide a then-innovative focused shopping experience with multiple stores within the same structure. Service areas were placed at the perimeter to maximize sales areas with open and flexible floorplans, but these cut off the relationship between levels and to the city outside.
Suspended ceilings of a single consistent height concealed the building services and the elaborate column and beam structural concrete frame. This anonymous, insular shopping environment lacked internal spatial connections and external visual relationships, and did not meet Uniqlo's aspiration for a customer-friendly flagship store.

Revealing a specific identity
A study of the original structural drawings and an early site visit revealed the practical beauty of the building's original concrete frame. Aiming to expose this 'found' construction both externally and internally, all extraneous elements such as cladding, suspended ceilings and additions were removed in an exercise of design through subtraction.
The resultant concrete grid is appropriated as a raw but muted framework to display Uniqlo's colorful products. An open network of beams and columns remains visible throughout the store’s interior and exterior.

To strengthen the holistic reading of the frame yet still provide for specificity, infills in a variety of materials are applied to each location and function: floors of stone, concrete, timber and metal; ceilings of colored panel and mirror; external facades of glass and cement studded with glass beads. The structural frame's strong orthogonal presence is humanized by its exceptions, lending unexpected character to the typical retail environment.
A precise surgery in parts of each floor slab create visual and spatial interconnections including double-height entrances and an interior quadruple-story plaza which extend the vitality and voyeurism of Ginza street life into the heart of the store. Remarkable views are attained from all retail floors.
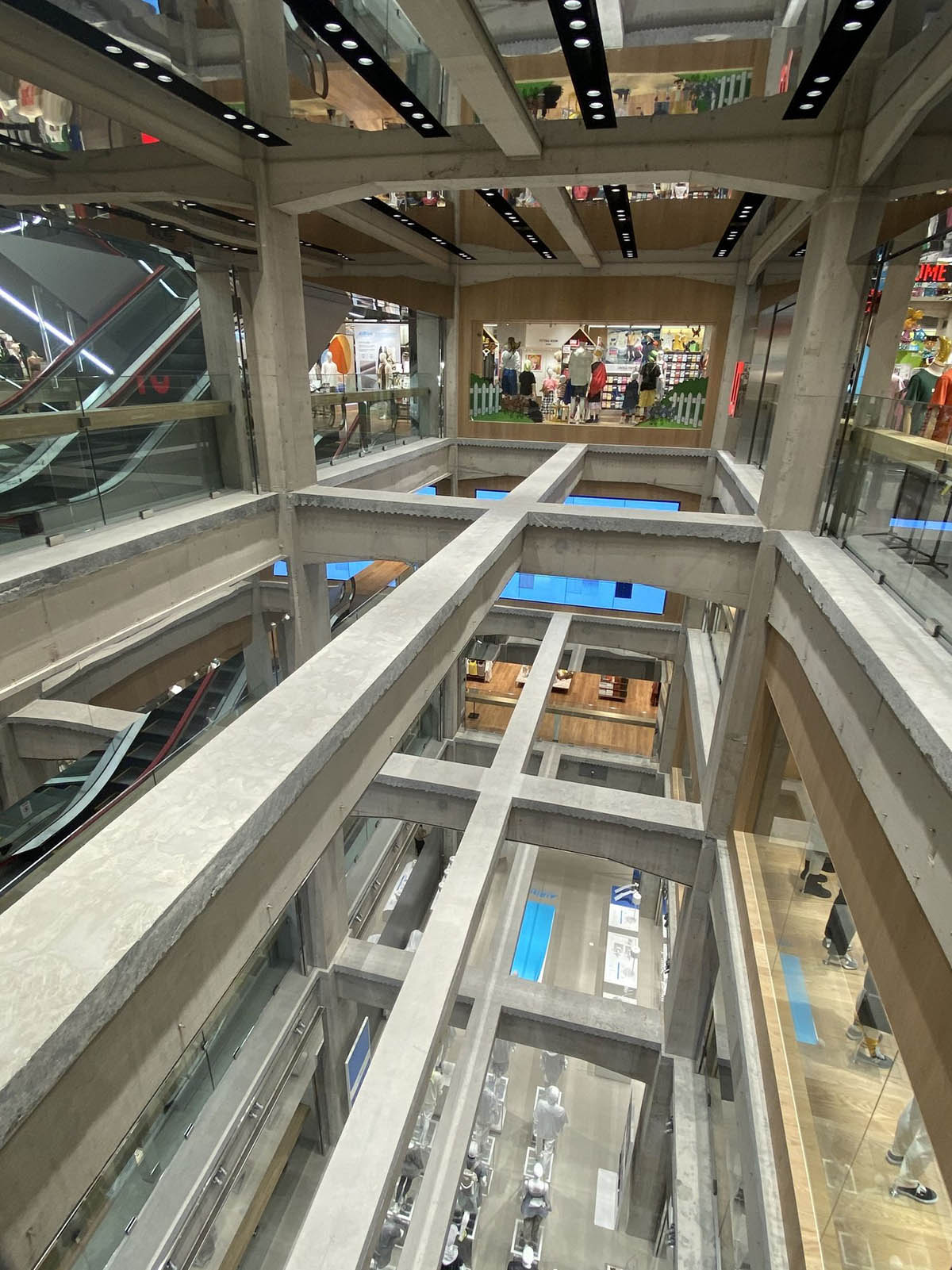

Existing beams span across the void, some with a mirrored underbelly to fragment its spatial perception. Where the slab is cut away, the raw edge of the concrete and steel is left exposed as a glimpse into the construction process. The "shelves" created by the concrete structure are either left open or punctuated with large wooden vitrines or digital screens, creating a central display and open gallery strategy for large site-specific installations.
Where the building meets the street, the exposed concrete frame becomes a type of "arcade" that welcomes shoppers off the street. The structure is left open at the two corner entrances, anticipating the tall plaza inside, with full-height glazed facades. Mirrored exterior ceilings reflect the interior displays, bringing Uniqlo's products into the visual periphery of pedestrians.

Distinct signage cubes – a reference to Uniqlo's graphic identity - define the outer edges of the building and mark Uniqlo's presence in the city from all sides. These cubes offer an opportunity to display dynamic graphics from designers and artists, becoming part of Ginza's active nighttime image.
Marronnier Gate returns to its essence: by stripping away a conventional retail interior, the functional beauty and simplicity of the building's original concrete skeleton is revealed and is used to generate new spatial excitement and possibilities. UNIQLO TOKYO and its beloved products are no longer hidden and now shared with the city outside.
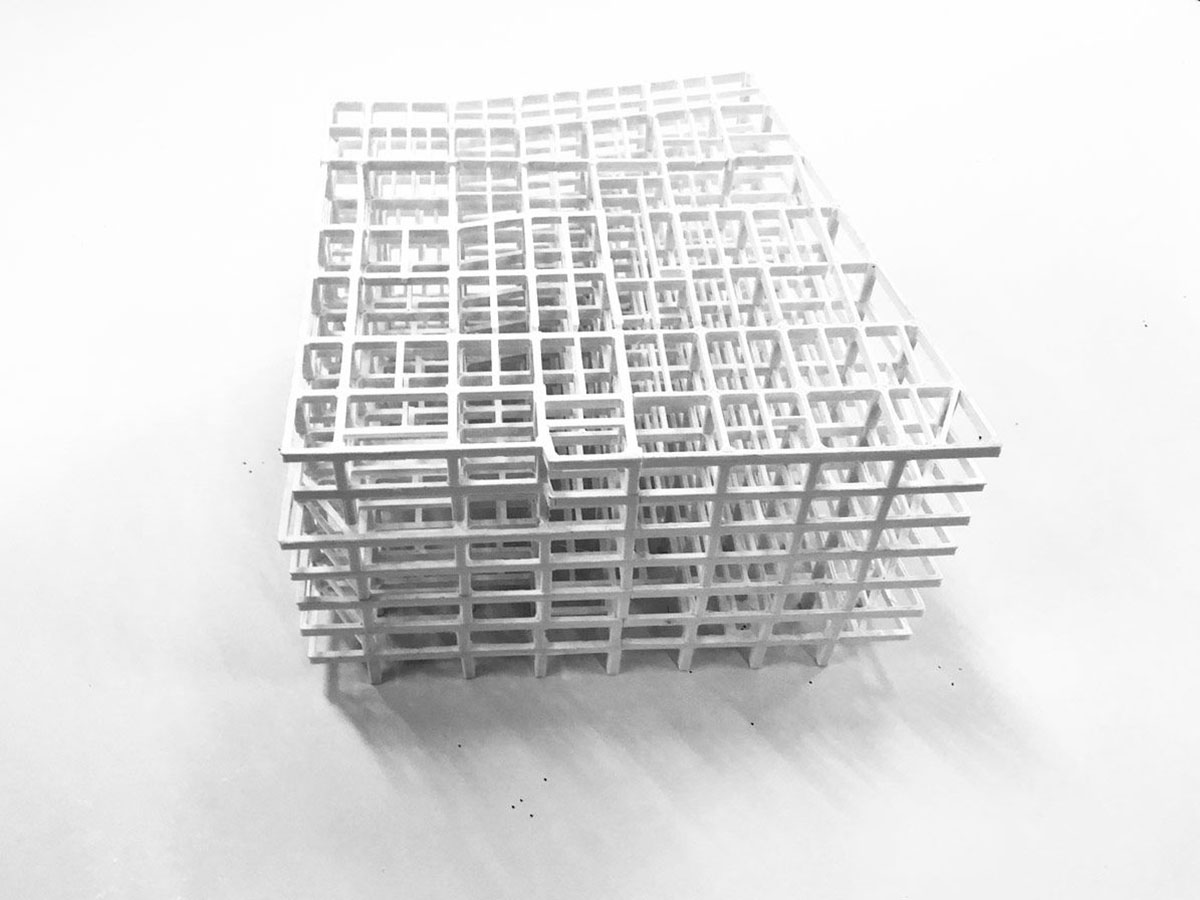
A diagram of gridal system
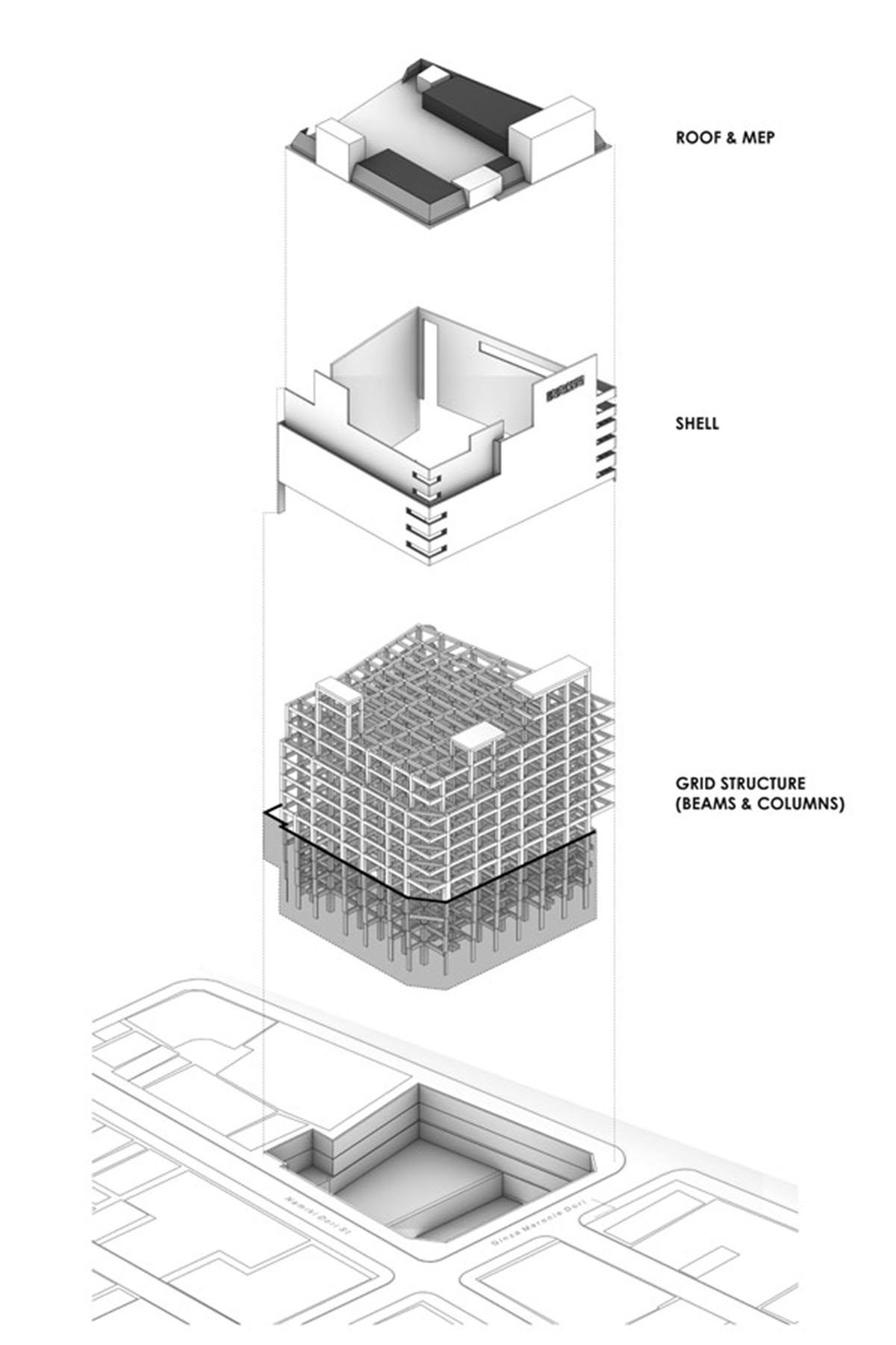
Axonometric drawing
Project facts
Herzog & de Meuron Project Team:
Partners: Jacques Herzog, Pierre de Meuron, Stefan Marbach (Partner in Charge)
Project Team: Dieter Mangold (Associate, Project Director), Yuko Himeno (Project Manager)
Michal Baurycza (Visualisations), Marcelo Bernardi (Associate), Edoardo Cappella, Teeranop Chamnong, Massimo Corradi, Josh Helin, Ryoko Ikeda, Ekaterina Nuzhdina, Lukasz Pawlicki, Pedro Peña Jurado, Alan Pülz, Jos Reinders, Kilian Schellenberger, Martin Schulte (Design Technologies), Florian Tropp.
Planning:
Executive Architect: Takenaka Corporation, Tokyo, Japan
Executive Architect (Interior): Nomura Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan
Structure Engineering: Takenaka Corporation, Tokyo, Japan
MEP Engineering: Takenaka Corporation, Tokyo, Japan
Specialist / Consulting:
Lighting: FDS Co.,Ltd., Tokyo, Japan
LED Signage: Hibino Chromatek Div., LED Solution Dept., Kanagawa, Japan
Digital Graphic Design: tha, Tokyo, Japan
Visualisations: Aron Lorincz Ateliers, Gödöllő, Hungary
Contractors:
Main Contractor: Takenaka Corporation, Tokyo, Japan
Main Contractor (Interior): Nomura Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan
Building data:
Site Area: 31,645 sqft / 2,940 sqm
Gross floor area (GFA): 248,204 sqft / 23,059 sqm
GFA above ground: 172,900 sqft / 16,063 sqm
GFA below ground: 75,304 sqft / 6,996 sqm
Outside Facilities: 5,360 sqft / 498 sqm
Number of levels: 11
Footprint: 27,598 sqft / 2,564 sqm
Building dimensions: Length 177 ft / 54 m; Width: 173 ft / 53 m; Height: 101 ft / 31 m
Gross volume (GV): 2,505,048 cbft / 70,935 cbm
Facade surface: 73,011 sqft / 6,783 sqm
Detailed data:
Complete Renovation GFA above ground: 8,575 sqm
Complete Renovation Facade Surface: 1,558 sqm
All images © Nacasa & Partners
All drawings © Herzog & de Meuron
> via Herzog & de Meuron
