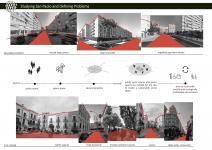
This project is an urban regeneration project of San Paolo district. San Paolo is located in the south-eastern part of Italy, 6 km away from Bari city center. It stands in very proximity to the industrial areas of Bari and Bari Karol Wojtyła Airport. Considering being located near the industrial zones of the city, the residential habitation emerges from the necessity of the social housing units for the working class of the Bari, which the construction of the residential housing blocks dates back to the 1960s and 1970s.
However, although these social housing blocks had been serving this purpose for some time in the past, meeting the very essential need of sheltering for working class; nowadays, it is clear that they are not adequate enough to provide a quality sustainable social life for the new community of today’s world. Therefore, this project aims to provide the habitants of the San Paolo district with socially and ecologically better sustainable, creating public spaces, social interactions, and more green open areas as primary design considerations.
Site Analysis:
According to the researches and site studies we have conducted before starting to the project, urban planning and architectural typologies plays a great role in defining spaces and qualities of those spaces which result in predefining the general life courses of the society living there. To exemplify, the historical city center of Bari proposes various spatial characteristics stimulating different social engagements such as public squares, green areas and parks, market places, large boulevards and small streets, shops, cafes, restaurants etc... However, in San Paolo district, it is not possible to see this much of variety in spatial typologies which the area only consists of repetitive apartment blocks, large boulevards and large unused left-over spaces.
Site Planning:
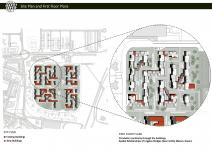
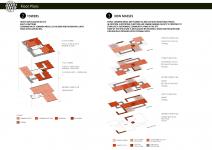
Therefore, corresponding to the need of new social spaces for the local community of San Paolo that has been living in the area for long times, the general design has initially started by the indication of the new typologies and functions that the site requires. According to survey we have conducted on the social needs of the communal living, a new and more comprehensive site plan is introduced. In this site plan, while the majority of the existing structures are being kept, some of them are eliminated in order to propose new typologies and articulations. One of the biggest concerns at this phase is to ensure that all local residences will be provided with their new houses with plenty of new spatial and social opportunities.
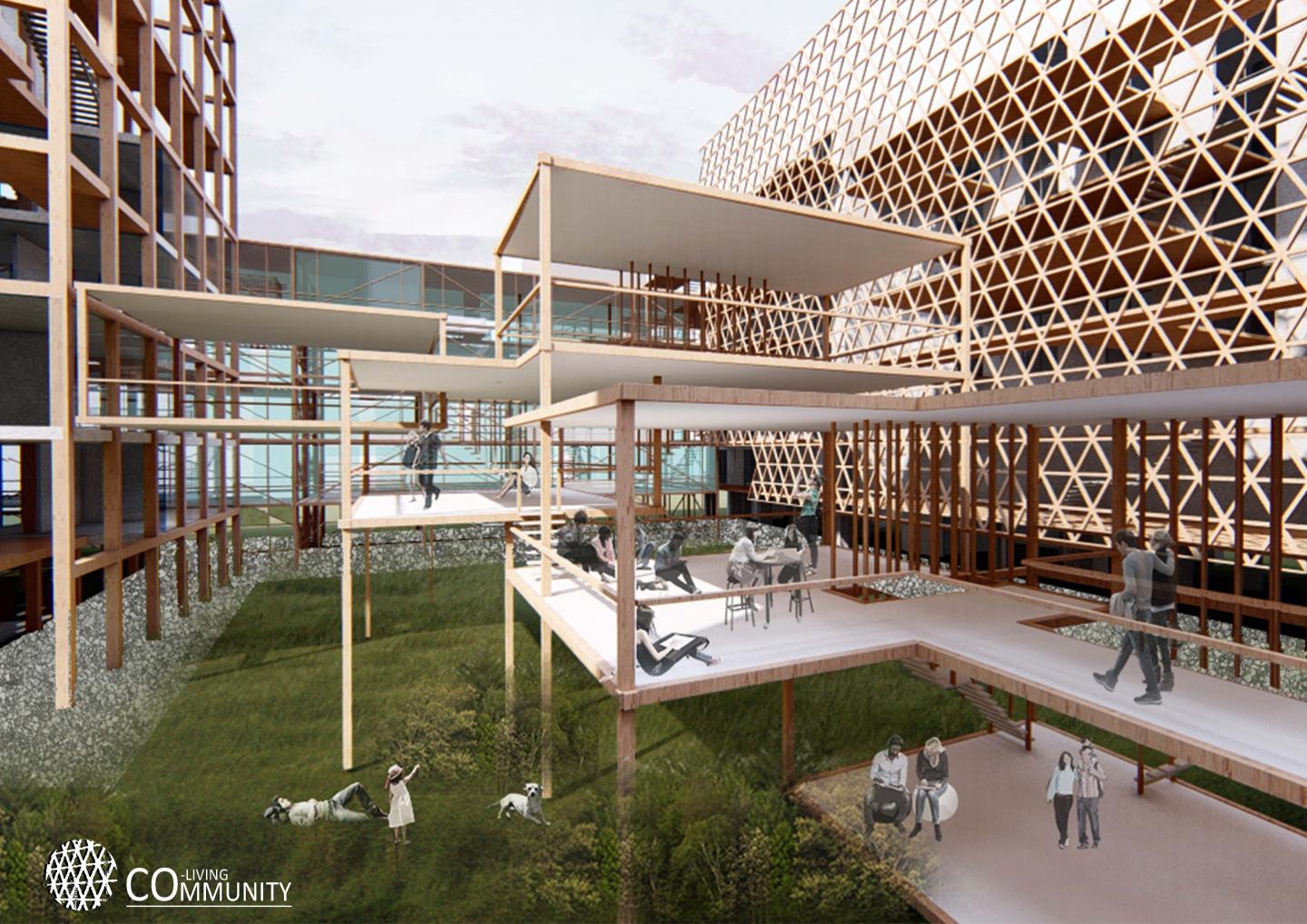
Outdoor Spaces: The new arrangement of the site typically allows to constitute courtyards in between the buildings hence defining and claiming the outdoor spaces for public use as well, on the contrary to the previous situation which the outdoor spaces were unused, leftover spaces. However, it is now obvious that outdoor spaces hold for a great importance for a healthy and livable neighborhood when it is designed accordingly. Also, the access of motor vehicles to the site is
restrained, so, it become possible to introduce greenery to these inner courtyards –outdoor spaces- thus providing a whole public use.
Forming&Programming: As a part of site planning, the area comprises of existing structures and newly-proposed ones: relatively higher structures called towers, new masses for communal spaces and bridge structures for increasing connections in the site. By these, the area becomes a place providing co-housing units and co-living areas, residential units, communal spaces for social activities and public spaces for gatherings.
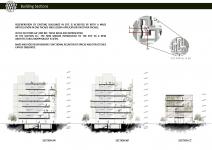
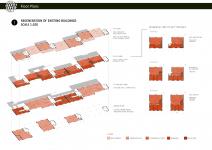
Regeneration of Existing Structures: Besides the new typologies introduced, how to transform the existing buildings in order to regenerate the structure was an important aspect of the project. The regeneration of the existing residential buildings is essential, considering that they did not provide any spatial characteristic or social opportunities. So, our strategy is the introduction of loggias on one façade and creating a mass articulation on the other façade. So, loggias could give the required social spaces for the residences and ease the neighbor encounters. Whereas, the mass articulation on the other façade provides the units with various spatial characteristics such as having a balcony or not, a green terrace, a shelter from direct sun light etc. Hence, with all these new implementations, the project design aims to provide the residences and users with a great and unique experiences in their houses, with plenty of social opportunities and well-thought spatial qualities.
Environmental Systems & Sustainability:
Besides all, environmental systems hold crucial importance in the design process of the area in order to ensure an ecologically sustainable environment. There are various environmental strategies utilized in this project for the maximum benefit of passive systems and energy needs. The primary choice for energy generation is by solar energy, supplied by photovoltaic panels placed on the roofs. Also, for a more efficient energy consumption, climate control is a crucial factor; which is tried to achieved by strategies like,
· solar gain control by shading patterns of mass articulations,
· a building skin creating a buffer zone in cold weather keeping the interior warm and providing efficient ventilation in summer,
· green terraces and green roof systems for passive cooling
· Urban agriculture areas for localized food production and better community engagement
In addition, water management systems are applied by careful implementation of rainwater harvesting system, reutilization of harvested rainwater in the residential units, recycling wastewater by greywater treatment systems and reusing it for flushing and irrigation.
2020
0000
The existing residential apartment blocks that are regenerated are reinforced concrete structures that had been constructed based on column and beam internal skeleton. Not having bearing walls or shear walls allowed us to easily transform and arrange the inner spaces according to the new design approaches.
However, in order to minimize the negative impact of concrete as a construction material, we have suggested different material catalogs for additional parts and new architectural typologies considering to opt for more environmental materials.
For the loggias and additional parts on mass articulation façades, we have utilized recyclable steel profiles. The reasoning for this material choice is due to the sustainability concerns and better material strength of steel. And, for the new urban agriculture masses and bridging masses, timber construction is chosen since the lightweight characteristics of timber better suit these relatively smaller structures and correspond to the inner functions, and most important, has less environmental footprint.
·Zeynep Berra Kirbasoglu
·Buket Gurbuz
Instructor: Francesco Defilippis
Favorited 1 times