World Architecture Awards 10+5+X Submissions
World Architecture Awards Submissions / 53rd Cycle
Vote button will be active when the World Architecture Community officially announces the Voting period on the website and emails. Please use this and the following pages to Vote if you are a signed-in registered member of the World Architecture Community and feel free to Vote for as many projects as you wish.
How to participate
WA Awards Submissions
WA Awards Winners
Architectural Projects Interior Design Projects
Architectural Projects Interior Design Projects
Bavi Heritage
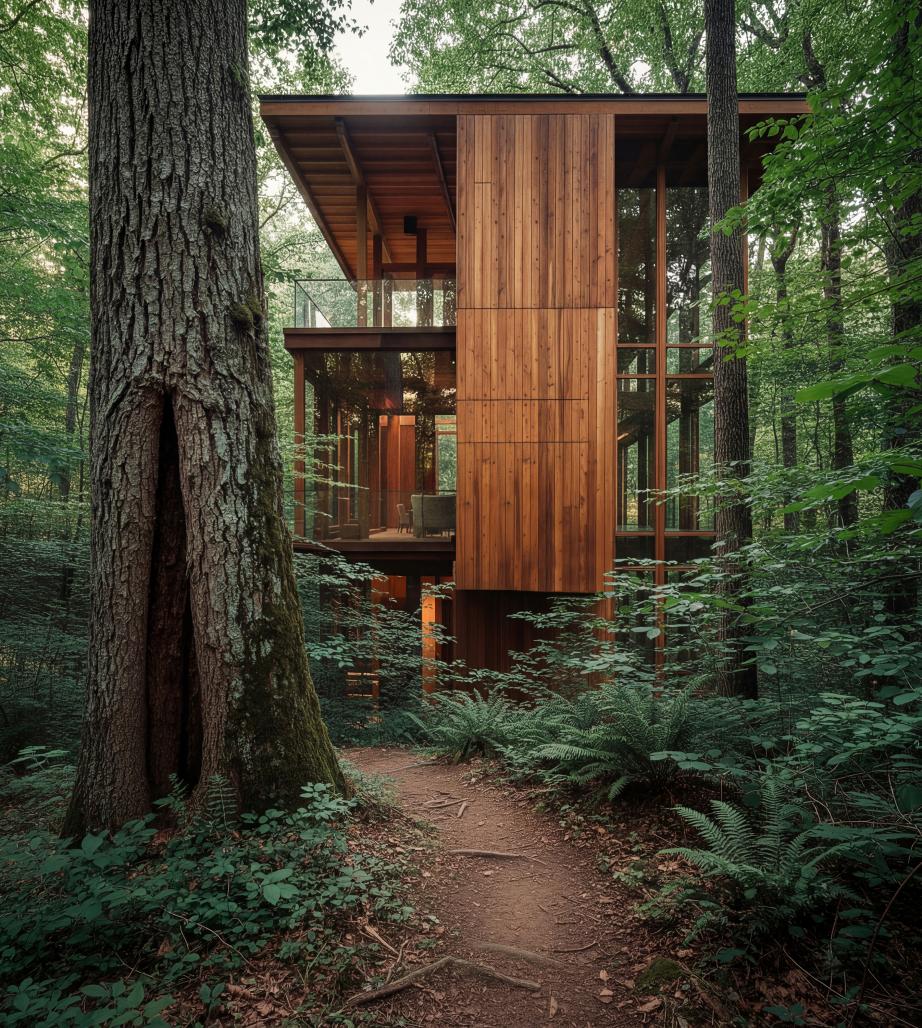


BAVI HERITAGE
Architecture Shaped by Limits
Key points
- Adaptive reuse of a former stone and woodworking complex embedded within an existing forest landscape in Ba Vì, Vietnam
- Architectural organization derived from inherited foundations, circulation routes, and terrain morphology
- Four pavilion typologies differentiated through topographical response and deliberate avoidance of existing mature trees
- Vertical spatial configuration minimizing footprint and preserving soil permeability
- Material juxtaposition revealing temporal continuity between retained stone structures and new concrete interventions
- Sustainability embedded within spatial and structural logic rather than applied as a separate technical layer
________________________________________
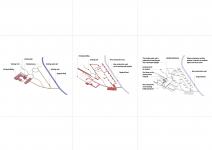
Bavi Heritage is a small-scale resort located within a planted forest of pine, oak, and native tall trees in Ba Vì, Vietnam. Before its transformation, the site functioned as a large stone and woodworking complex, consisting of workshops and storage buildings constructed from local stone and plantation timber. More than a physical condition, the site embodies a layered memory of manual labor, craftsmanship, and generational continuity tied to the land.
Rather than approaching the project as a new resort inserted into nature, Bavi Heritage is conceived as a process of spatial reconfiguration, in which contemporary architecture is shaped by pre-existing ecological, structural, and cultural limits. The central question of the project is not one of form-making, but whether architecture can emerge without severing the continuity of place.
The design positions heritage as a living structure rather than a static artifact. Foundations, stone walls, circulation routes, and spatial logic inherited from decades of industrial use are treated as active design frameworks. Instead of demolition and replacement, the project adopts a strategy of minimal intervention and adaptive reuse, allowing existing structures to guide new architectural organization. Key functions such as reception, back-of-house, and technical spaces are built directly upon former workshop foundations, significantly reducing excavation, construction waste, and embodied energy while preserving the site’s topographical continuity.
Architecturally, the project does not seek to conceal the passage of time. Rough stone walls are retained and reinforced, deliberately juxtaposed with new exposed concrete structures. The contrast between old and new is left legible, forming a spatial dialogue rather than a seamless fusion. History is not represented symbolically; it is revealed through material presence and structural continuity.
One of the project’s primary challenges lies in negotiating the tension between resort development and forest preservation. The site is defined by dense vegetation, complex root systems, and a sensitive microclimate—conditions typically incompatible with conventional hospitality planning. Instead of imposing an idealized master plan, the design accepts ecological constraints as formative parameters. Accommodation units, referred to as Pavilions, are placed exclusively within existing natural clearings identified through on-site surveys.
Four pavilion types are developed in direct response to variations in terrain and the precise location of existing trees, allowing each unit to adjust its form and placement in order to avoid root systems and minimize disturbance to the natural ground condition.
To minimize ground disturbance, they are organized vertically rather than horizontally, reducing footprint while maintaining spatial efficiency. Access paths remain compacted earth rather than hard paving, preserving soil permeability and terrain continuity. Controlled inconvenience is embraced as a conscious architectural choice rather than a compromise.
In this sense, the forest is not treated as a backdrop but as a structural agent that shapes architectural decisions. The buildings do not compete with their environment; they are configured by it.
A parallel challenge involves the reuse of an industrial heritage lacking conventional monumentality. The former workshops—raw, utilitarian, and visually understated—could easily be dismissed as obstacles to new development. Rather than aestheticizing or erasing them, the project focuses on translating their spatial and structural logic into a contemporary framework. Former industrial circulation routes are reinterpreted as long, naturally lit corridors that function as primary spatial arteries, enhancing cross-ventilation and moderating the tropical microclimate.
Sustainability in Bavi Heritage is not addressed as a separate technical layer, but as a direct outcome of design logic. The reuse of existing structures reduces material consumption and construction energy; open and transitional spaces limit reliance on mechanical cooling; local stone and plantation timber minimize transportation impact and enhance climatic adaptability. Rainwater is collected, filtered, and reused through courtyards and gardens, integrated with a nearly century-old well that historically functioned as the site’s hydrological center. Together, these elements form a closed-loop water system supporting both daily use and landscape irrigation.
At the location of the former family house, a Private Zen House is constructed as an intimate architectural layer dedicated to meditation and retreat. Detached from commercial programmatic demands, this building sustains a personal and spiritual connection between the owner and the land. The upper meditation space opens directly to the forest canopy, allowing light, wind, and ambient sound to become integral components of the architectural experience.
Through these decisions, Bavi Heritage deliberately redefines the notion of luxury in resort architecture. Value is not derived from material opulence or scale, but from restraint, authenticity, and proximity to nature. Architecture here acts as an enabling framework rather than a dominating presence, allowing users to perceive their relationship with landscape, memory, and time.
Bavi Heritage ultimately proposes architecture as a practice of acceptance rather than control. By working within ecological, structural, and cultural limits, the project demonstrates that architectural quality can emerge not from overcoming constraints, but from allowing those constraints to shape space, experience, and meaning.
Project name: BAVI HERITAGE
Location: Vietnam
Site area: 9,5ha
GFA: 13.971,7m2
Density: 9,6%
Building function: Resort, Spa(Jjimjilbang), Restaurant, Workshop space, Resort accommodation in pavilions.
Principal Architect: Nguyễn Thái Sơn
Design team: David Lee, Sophia muller, Nguyễn Thành Phong
Green building team: SAA Green team
Structural Design Engineer: Hà Văn Kha
MEP Design Engineer: Trịnh Tiến Đông
Architecture Shaped by Limits
Key points
- Adaptive reuse of a former stone and woodworking complex embedded within an existing forest landscape in Ba Vì, Vietnam
- Architectural organization derived from inherited foundations, circulation routes, and terrain morphology
- Four pavilion typologies differentiated through topographical response and deliberate avoidance of existing mature trees
- Vertical spatial configuration minimizing footprint and preserving soil permeability
- Material juxtaposition revealing temporal continuity between retained stone structures and new concrete interventions
- Sustainability embedded within spatial and structural logic rather than applied as a separate technical layer
________________________________________
Bavi Heritage is a small-scale resort located within a planted forest of pine, oak, and native tall trees in Ba Vì, Vietnam. Before its transformation, the site functioned as a large stone and woodworking complex, consisting of workshops and storage buildings constructed from local stone and plantation timber. More than a physical condition, the site embodies a layered memory of manual labor, craftsmanship, and generational continuity tied to the land.
Rather than approaching the project as a new resort inserted into nature, Bavi Heritage is conceived as a process of spatial reconfiguration, in which contemporary architecture is shaped by pre-existing ecological, structural, and cultural limits. The central question of the project is not one of form-making, but whether architecture can emerge without severing the continuity of place.
The design positions heritage as a living structure rather than a static artifact. Foundations, stone walls, circulation routes, and spatial logic inherited from decades of industrial use are treated as active design frameworks. Instead of demolition and replacement, the project adopts a strategy of minimal intervention and adaptive reuse, allowing existing structures to guide new architectural organization. Key functions such as reception, back-of-house, and technical spaces are built directly upon former workshop foundations, significantly reducing excavation, construction waste, and embodied energy while preserving the site’s topographical continuity.
Architecturally, the project does not seek to conceal the passage of time. Rough stone walls are retained and reinforced, deliberately juxtaposed with new exposed concrete structures. The contrast between old and new is left legible, forming a spatial dialogue rather than a seamless fusion. History is not represented symbolically; it is revealed through material presence and structural continuity.
One of the project’s primary challenges lies in negotiating the tension between resort development and forest preservation. The site is defined by dense vegetation, complex root systems, and a sensitive microclimate—conditions typically incompatible with conventional hospitality planning. Instead of imposing an idealized master plan, the design accepts ecological constraints as formative parameters. Accommodation units, referred to as Pavilions, are placed exclusively within existing natural clearings identified through on-site surveys.
Four pavilion types are developed in direct response to variations in terrain and the precise location of existing trees, allowing each unit to adjust its form and placement in order to avoid root systems and minimize disturbance to the natural ground condition.
To minimize ground disturbance, they are organized vertically rather than horizontally, reducing footprint while maintaining spatial efficiency. Access paths remain compacted earth rather than hard paving, preserving soil permeability and terrain continuity. Controlled inconvenience is embraced as a conscious architectural choice rather than a compromise.
In this sense, the forest is not treated as a backdrop but as a structural agent that shapes architectural decisions. The buildings do not compete with their environment; they are configured by it.
A parallel challenge involves the reuse of an industrial heritage lacking conventional monumentality. The former workshops—raw, utilitarian, and visually understated—could easily be dismissed as obstacles to new development. Rather than aestheticizing or erasing them, the project focuses on translating their spatial and structural logic into a contemporary framework. Former industrial circulation routes are reinterpreted as long, naturally lit corridors that function as primary spatial arteries, enhancing cross-ventilation and moderating the tropical microclimate.
Sustainability in Bavi Heritage is not addressed as a separate technical layer, but as a direct outcome of design logic. The reuse of existing structures reduces material consumption and construction energy; open and transitional spaces limit reliance on mechanical cooling; local stone and plantation timber minimize transportation impact and enhance climatic adaptability. Rainwater is collected, filtered, and reused through courtyards and gardens, integrated with a nearly century-old well that historically functioned as the site’s hydrological center. Together, these elements form a closed-loop water system supporting both daily use and landscape irrigation.
At the location of the former family house, a Private Zen House is constructed as an intimate architectural layer dedicated to meditation and retreat. Detached from commercial programmatic demands, this building sustains a personal and spiritual connection between the owner and the land. The upper meditation space opens directly to the forest canopy, allowing light, wind, and ambient sound to become integral components of the architectural experience.
Through these decisions, Bavi Heritage deliberately redefines the notion of luxury in resort architecture. Value is not derived from material opulence or scale, but from restraint, authenticity, and proximity to nature. Architecture here acts as an enabling framework rather than a dominating presence, allowing users to perceive their relationship with landscape, memory, and time.
Bavi Heritage ultimately proposes architecture as a practice of acceptance rather than control. By working within ecological, structural, and cultural limits, the project demonstrates that architectural quality can emerge not from overcoming constraints, but from allowing those constraints to shape space, experience, and meaning.
Project name: BAVI HERITAGE
Location: Vietnam
Site area: 9,5ha
GFA: 13.971,7m2
Density: 9,6%
Building function: Resort, Spa(Jjimjilbang), Restaurant, Workshop space, Resort accommodation in pavilions.
Principal Architect: Nguyễn Thái Sơn
Design team: David Lee, Sophia muller, Nguyễn Thành Phong
Green building team: SAA Green team
Structural Design Engineer: Hà Văn Kha
MEP Design Engineer: Trịnh Tiến Đông
Chanakya x Dior


Presenting a project born out of collaboration between Dior and Indian venture Chanakya, Chanakya X Dior celebrates local craftsmanship and design expertise. Focusing on locally made fabrics with innovative design the project is an unique architectural marvel.
Nestled in the vibrant city of Mumbai, the project serves as a dynamic public infrastructure, offering a diverse array of multi-program spaces. From exhibition centers to learning hubs, activity zones to experiential spaces, the design caters to a wide range of interests and activities.
Open to sky entry courts coupled with internal light courts create a typology that is closely connected with the outdoors Infused with terraced gardens, cascading roof greens, large trees and shrubs, the design helps to generate a microclimate that keeps the temperatures in control throughout the year. The diverse program for the project is aesthetically held together by a mesh that envelopes the built forms Central courtyards within the built masses hold all the facilities together. Conceived as a place for the community to come together and participate in events that celebrate the master art and crafts.
Inspired by fabric design, the structure's form takes on a dynamic shape, incorporating a parametric facade. This innovative design blurs the lines between inside and outside, creating seamless transitions and stunning experiences for visitors. The building prioritizes sustainability by employing locally manufactured materials for construction.
Its innovative design features facade cladding using brick throughout the structure, ensuring durability and aesthetic appeal. The entire mass is enveloped in an aluminum pipe framework, enabling the realization of a parametric form and shape. This strategic integration of materials and design not only enhances the building's sustainability but also exemplifies a commitment to environmental consciousness and architectural innovation.
Principal Archiects - Anand Menon, Shobhan Kothari
Team - Manish Patil, Dinesh Thakur
Nestled in the vibrant city of Mumbai, the project serves as a dynamic public infrastructure, offering a diverse array of multi-program spaces. From exhibition centers to learning hubs, activity zones to experiential spaces, the design caters to a wide range of interests and activities.
Open to sky entry courts coupled with internal light courts create a typology that is closely connected with the outdoors Infused with terraced gardens, cascading roof greens, large trees and shrubs, the design helps to generate a microclimate that keeps the temperatures in control throughout the year. The diverse program for the project is aesthetically held together by a mesh that envelopes the built forms Central courtyards within the built masses hold all the facilities together. Conceived as a place for the community to come together and participate in events that celebrate the master art and crafts.
Inspired by fabric design, the structure's form takes on a dynamic shape, incorporating a parametric facade. This innovative design blurs the lines between inside and outside, creating seamless transitions and stunning experiences for visitors. The building prioritizes sustainability by employing locally manufactured materials for construction.
Its innovative design features facade cladding using brick throughout the structure, ensuring durability and aesthetic appeal. The entire mass is enveloped in an aluminum pipe framework, enabling the realization of a parametric form and shape. This strategic integration of materials and design not only enhances the building's sustainability but also exemplifies a commitment to environmental consciousness and architectural innovation.
Principal Archiects - Anand Menon, Shobhan Kothari
Team - Manish Patil, Dinesh Thakur
Conceptual Planning Scheme for Chongqing University's Wisdom Valley Campus
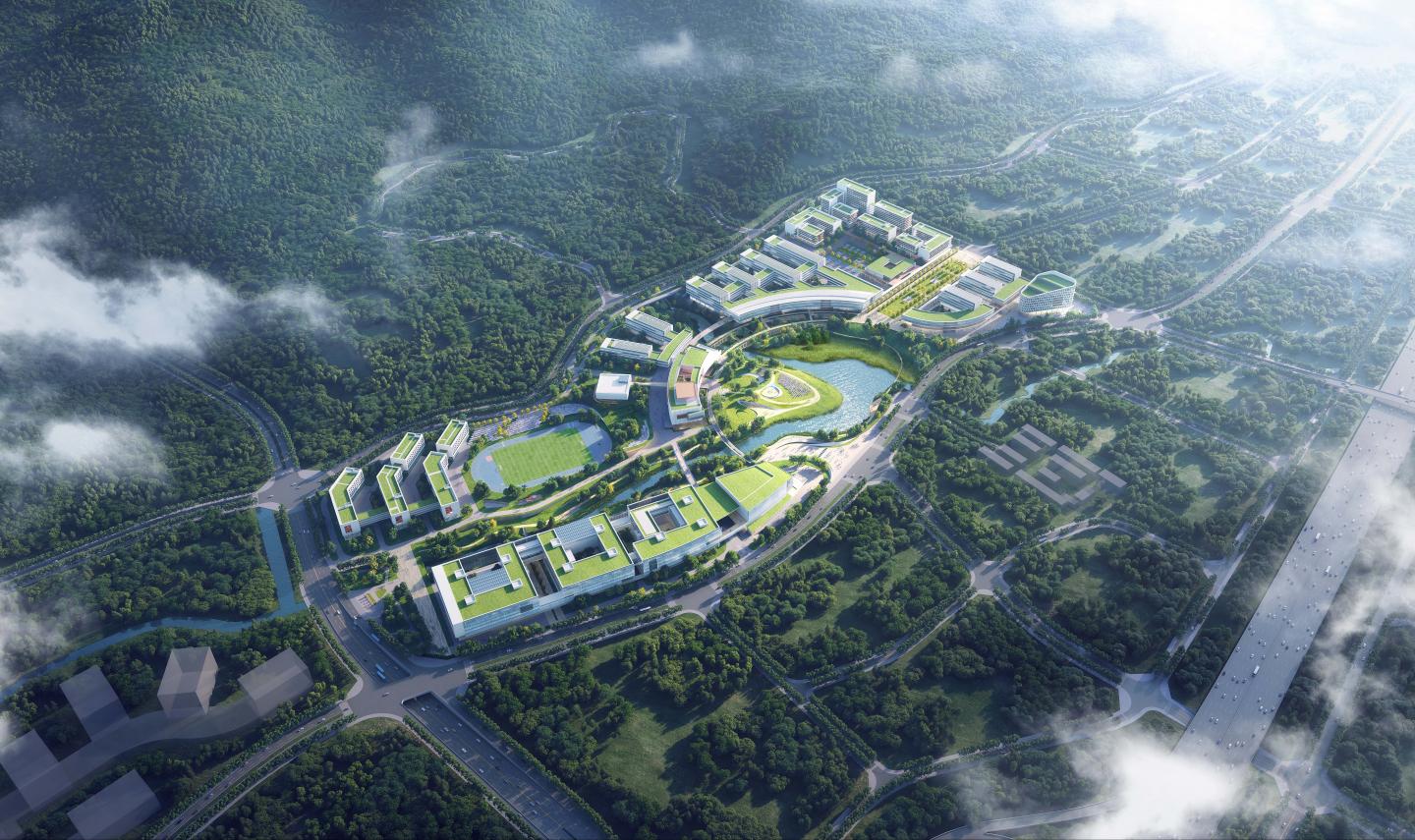


As the new campus for one of the best universities in Western China, designed to accommodate 10,000 faculty and students in the future, the primary design goal for the Chongqing University Wisdom Valley Campus is to create a future campus that integrates nature, ecology, education, technology, and innovation. Concurrently, the campus is intended to serve as a vital, organic component of the Chongqing Science City, a major new science and technology hub in Western China.
The project site reflects the natural geographical characteristics of Chongqing, the world-renowned mountain metropolis: the environment of coexisting mountains and water fostered the development of this site. Jinyun Mountain on the west side serves as the backdrop for the campus with its continuous mountain ranges. The confluence of the Huxi River and Yangjiagou Stream forms a natural peninsula known as Qinglongzui.
The master plan is dedicated to transforming the conventional closed university campus model. The university of the future belongs not only to its faculty and students but also to the city. The campus layout, characterized by a well-balanced mix of density and open, grand gestures, creates an open space facing the city in the pre-campus area on the east side, forming a massive C-shaped "Academic Loop." This loop connects the various campus zones while actively engaging the city, promoting interaction and co-existence.
Under the principle of "Design Following Nature," the naturally formed confluence of the two rivers within the campus is enlarged into an ecological peninsula. This peninsula is designated as the Campus Energetic Core(CEC), housing landmark buildings such as key laboratories, the library, and the auditorium. Together with natural elements like the lake, sparse woods, and lawns, they form the ecological heart of the campus.
The design creates a campus spatial model that breaks down disciplinary barriers. The Academic Loop consists of a series of public classrooms and laboratories, offering high efficiency and intensive use. Faculty and students from colleges such as Optoelectronic Engineering, Microelectronics and Communication Engineering, and Intelligent Connected Vehicles will study here, promoting disciplinary integration and cross-disciplinary research.
Furthermore, the Academic Loop is also a Three-Dimensional Efficiency Ring. By scientifically utilizing the elevation differences through a three-dimensional integrated transportation strategy, it connects three distinct spatial layers: the underground vehicular flow, the ground-level pedestrian flow, and the overhead academic public platform.
The longitudinal campus public space running north-south through the campus forms two major campus composite axes, linking teaching and research, health and sports, and residential living. The Waterfront Public Vitality Belt on the south shapes both banks of the Huxi River into a water-friendly social interaction space. The research and office buildings on the east bank adopt a modular spatial model to meet flexible development needs. The Northern Campus Boulevard carries the campus's century-long history, incorporating cultural landscapes to organically integrate culture and history with the modern campus space.
Site Area: 5,900,000㎡ (39.3 hectares)
Construction Gross Area: 465,000㎡
Chu Donozhu, Yang Yang, Chu Longfei, Guan Shihan, Yang Yue, Yu Yan, Zheng wenchong, Deng Yuwen, Liu Xueyang, Zhou lingzhi, Shen Qingzhi, Li Baopeng, Zhang Songming, Wang Dagang
The project site reflects the natural geographical characteristics of Chongqing, the world-renowned mountain metropolis: the environment of coexisting mountains and water fostered the development of this site. Jinyun Mountain on the west side serves as the backdrop for the campus with its continuous mountain ranges. The confluence of the Huxi River and Yangjiagou Stream forms a natural peninsula known as Qinglongzui.
The master plan is dedicated to transforming the conventional closed university campus model. The university of the future belongs not only to its faculty and students but also to the city. The campus layout, characterized by a well-balanced mix of density and open, grand gestures, creates an open space facing the city in the pre-campus area on the east side, forming a massive C-shaped "Academic Loop." This loop connects the various campus zones while actively engaging the city, promoting interaction and co-existence.
Under the principle of "Design Following Nature," the naturally formed confluence of the two rivers within the campus is enlarged into an ecological peninsula. This peninsula is designated as the Campus Energetic Core(CEC), housing landmark buildings such as key laboratories, the library, and the auditorium. Together with natural elements like the lake, sparse woods, and lawns, they form the ecological heart of the campus.
The design creates a campus spatial model that breaks down disciplinary barriers. The Academic Loop consists of a series of public classrooms and laboratories, offering high efficiency and intensive use. Faculty and students from colleges such as Optoelectronic Engineering, Microelectronics and Communication Engineering, and Intelligent Connected Vehicles will study here, promoting disciplinary integration and cross-disciplinary research.
Furthermore, the Academic Loop is also a Three-Dimensional Efficiency Ring. By scientifically utilizing the elevation differences through a three-dimensional integrated transportation strategy, it connects three distinct spatial layers: the underground vehicular flow, the ground-level pedestrian flow, and the overhead academic public platform.
The longitudinal campus public space running north-south through the campus forms two major campus composite axes, linking teaching and research, health and sports, and residential living. The Waterfront Public Vitality Belt on the south shapes both banks of the Huxi River into a water-friendly social interaction space. The research and office buildings on the east bank adopt a modular spatial model to meet flexible development needs. The Northern Campus Boulevard carries the campus's century-long history, incorporating cultural landscapes to organically integrate culture and history with the modern campus space.
Site Area: 5,900,000㎡ (39.3 hectares)
Construction Gross Area: 465,000㎡
Chu Donozhu, Yang Yang, Chu Longfei, Guan Shihan, Yang Yue, Yu Yan, Zheng wenchong, Deng Yuwen, Liu Xueyang, Zhou lingzhi, Shen Qingzhi, Li Baopeng, Zhang Songming, Wang Dagang
Eternity Residence
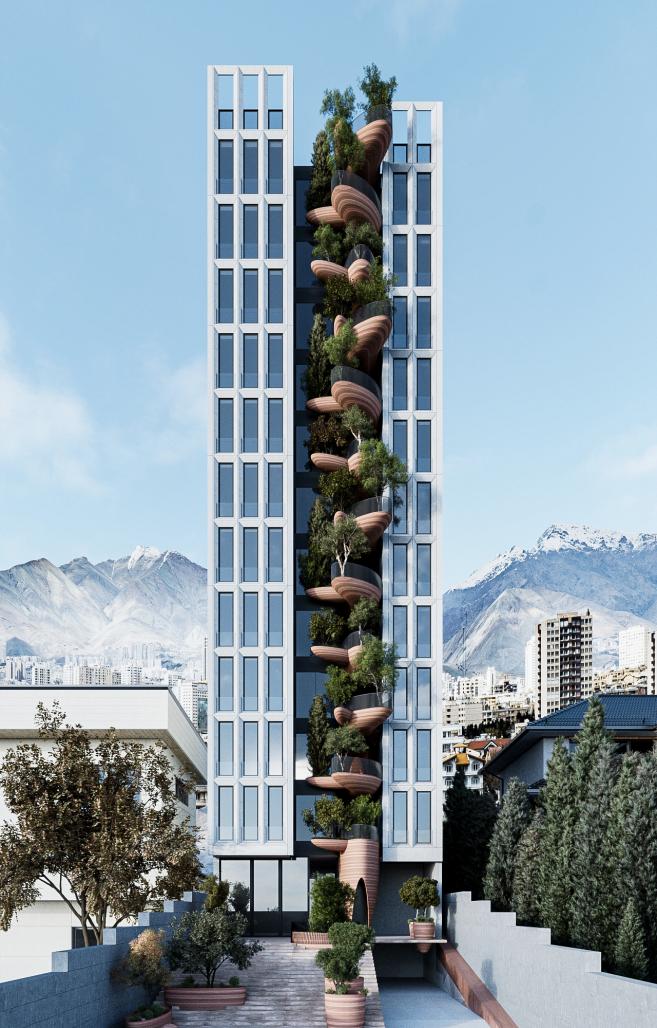


This project, located in Tehran- Iran, is formed as a Contemporary Interpretation of Vernacular Architecture, aiming to redefine the relationship between humans and nature and to revive the forgotten role of the courtyard in contemporary residential architecture.
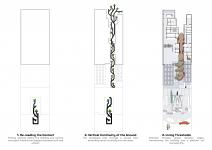
In this design, the courtyard is defined not merely as an open space, but as a central and organizing element that simultaneously enhances the dynamism of diverse functions, the quality of living, and human interactions.
The central courtyard of the residential units is vertically extended through the heart of the building. By creating spatial continuity between the main courtyard of the project and the upper floors, the presence of nature is expanded into all spaces.
The geometry of the residential spaces is derived from orthogonal forms based on everyday functions, expressing simplicity and clarity. In contrast, the central courtyard, inspired by natural forms and a fluid and dynamic atmosphere, is shaped through curved geometries. This integration of form and function transforms the building from a static volume into an active element within the urban fabric, reducing visual tension, enhancing ecological interaction, and promoting users’ mental well-being, truly making a house a home.
The placement of vegetation within the central courtyard, together with Human Scale proportions, creates a living and dynamic environment inspired by nature and executed according to Iranian architectural patterns using baked bricks, reflecting Materiality & Local Identity. This strategy contributes to climatic moderation, improved natural ventilation, and the enhancement of interior living quality.
Natural light, a key design element, is intentionally guided in a controlled and purposeful manner, penetrating deep into the interior spaces.
In this project, guided by a social and human-centered design approach, the rooftop garden was carefully crafted as a communal space that fosters meaningful social interactions among residents while enhancing the building’s shared amenities.
Ultimately, this project presents a contemporary model of residential architecture that, through the courtyard, nature, and spatial proportions, establishes a meaningful connection between human, architecture, and the city, demonstrating a clear Design Intent rooted in Design Necessity.
Total Built Area: 8,600 m²
Site Area: 1065 m²
Location: No. 33, 17th Alley, Velenjak Street, Tehran, Iran
Spatial Organization: twelve above-ground levels and four basement levels. A ground-floor lobby, eleven flat residential floors. The basements include three levels for parking and one level for amenities such as party room. This vertical distribution ensures independence for each unit while keeping them connected under one roof.
Design team: Seyed Amirhossein Sahiholnasab , Alireza Ghaffari , Amirhossein Kholghi
Graphic: Mahdi Ghafouri
In this design, the courtyard is defined not merely as an open space, but as a central and organizing element that simultaneously enhances the dynamism of diverse functions, the quality of living, and human interactions.
The central courtyard of the residential units is vertically extended through the heart of the building. By creating spatial continuity between the main courtyard of the project and the upper floors, the presence of nature is expanded into all spaces.
The geometry of the residential spaces is derived from orthogonal forms based on everyday functions, expressing simplicity and clarity. In contrast, the central courtyard, inspired by natural forms and a fluid and dynamic atmosphere, is shaped through curved geometries. This integration of form and function transforms the building from a static volume into an active element within the urban fabric, reducing visual tension, enhancing ecological interaction, and promoting users’ mental well-being, truly making a house a home.
The placement of vegetation within the central courtyard, together with Human Scale proportions, creates a living and dynamic environment inspired by nature and executed according to Iranian architectural patterns using baked bricks, reflecting Materiality & Local Identity. This strategy contributes to climatic moderation, improved natural ventilation, and the enhancement of interior living quality.
Natural light, a key design element, is intentionally guided in a controlled and purposeful manner, penetrating deep into the interior spaces.
In this project, guided by a social and human-centered design approach, the rooftop garden was carefully crafted as a communal space that fosters meaningful social interactions among residents while enhancing the building’s shared amenities.
Ultimately, this project presents a contemporary model of residential architecture that, through the courtyard, nature, and spatial proportions, establishes a meaningful connection between human, architecture, and the city, demonstrating a clear Design Intent rooted in Design Necessity.
Total Built Area: 8,600 m²
Site Area: 1065 m²
Location: No. 33, 17th Alley, Velenjak Street, Tehran, Iran
Spatial Organization: twelve above-ground levels and four basement levels. A ground-floor lobby, eleven flat residential floors. The basements include three levels for parking and one level for amenities such as party room. This vertical distribution ensures independence for each unit while keeping them connected under one roof.
Design team: Seyed Amirhossein Sahiholnasab , Alireza Ghaffari , Amirhossein Kholghi
Graphic: Mahdi Ghafouri
Incek Villa Settlement
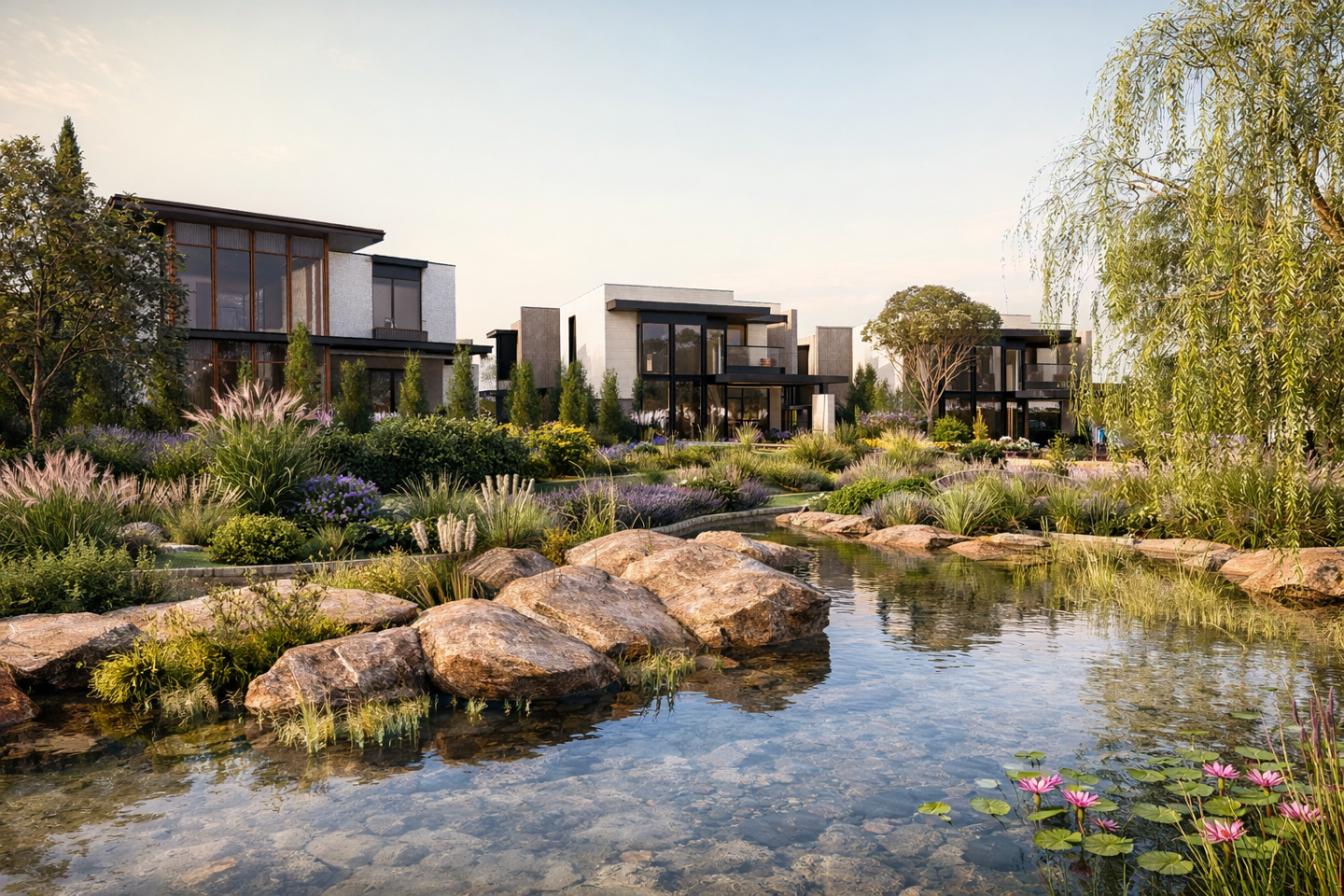


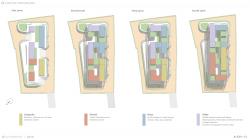
The project proposes a holistic settlement model that redefines contemporary living practices through its strong relationship with nature. The starting point of the design was the existing topographical character of the site, its natural thresholds, and landscape continuity. Rather than imposing an object onto the land, the development strategy follows the existing morphology and evolves with it. This approach establishes a continuous relationship between built masses and open spaces, creating a settlement structure in which the boundaries between natural and built environments become permeable.
In this context, the settlement is conceived not merely as a parcel containing residential units, but as a micro-community defined by its internal dynamics, articulated open spaces, and social focal points. Landscape operates not as a background element but as the primary organizer of the design, shaping spatial experience through squares, gardens, and pedestrian axes.
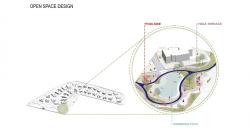
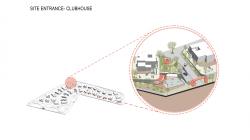
The social facility located along the main entrance axis is treated not only as a functional unit but as a threshold space that guides user experience and defines the public character of the settlement. Composed of programmatic elements such as the clubhouse, swimming pool, and yoga terrace, this structure forms a focal point that encourages social interaction and supports healthy living practices. Its positioning and spatial organization establish a strong visual and physical relationship with the landscape while also functioning as an orienting element within the overall layout.
The open space system shaped around the social facility is defined through named gathering areas such as Nefes Düzü Square, Itır Düzü Square, and Kuyu Düzü Square, reinforcing spatial memory and identity. These areas function not only as transition points but as social thresholds that enable encounters, pause, rest, and collective presence.
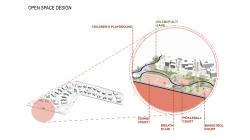
The open space network is conceived as an active spatial backbone that guides design decisions rather than a passive landscape surrounding the buildings. Designed for different age groups and usage scenarios, these open areas create an experiential network that supports interaction in addition to organizing circulation. Children’s playgrounds, multi-purpose sports courts, and pedestrian routes are structured as components of this continuity, establishing a balanced system between movement and pause, individual use and collective experience.
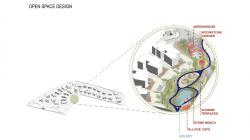
The existing greenhouse on the site, which contains endemic plant species, has been preserved, and the settlement layout has been shaped with respect to this productive landscape. In this way, the design does not impose a new order onto the land but develops in continuity with existing natural and local values. Lavender fields, small groves, stone seating elements, and defined resting pockets further create a sequence of open spaces offering experiences at different scales.
Residential units are positioned in accordance with the topography and orientation strategies to maximize daylight, natural ventilation, and views. Across different villa typologies, internal courtyards, stone-paved areas, and semi-private outdoor spaces complement the main gardens, strengthening spatial continuity. This approach defines housing not solely through enclosed interior organization, but through the relationship between indoor, semi-open, and open spaces, offering a dynamic living model.
Each unit ensures individual privacy, while the positioning of volumes and façade orientations carefully prevent direct visual intrusion between neighboring parcels. Thus, private living spaces are protected while a balanced relationship with collective life is maintained through semi-public open areas and a permeable landscape structure. Rather than sharply separating individual and communal life, the design produces a multi-layered spatial experience that defines transitions between them.
The project is not merely a physical settlement proposal, but a living model that redefines the relationship between nature, user, and space. Through spatial diversity, topography-sensitive placement strategies, and a landscape-oriented design approach, the settlement operates as a sustainable ecological and social system within itself. Within the intensity of contemporary urban life, it offers a secure and controlled framework while creating an inward-oriented world that strengthens social bonds and maintains a continuous connection with nature.
This holistic approach establishes a balanced relationship between the pace of urban life and the continuity of nature, providing users with an enriched living experience at both individual and collective scales.
Site Area: 38909,00m²
Gross Floor Area: 22255,75m²
Orçun Ersan, Sedef Yıldız, İrem Ardıç, İlginay Akyol, Hilal Delibaş, Gökçe Yıldız, Oğuzhan Çelik, Feyza Nur Şimşek, Fethi Ahmet Çelik, Feyza Nur Tekdemir, Simge Nur Topuz, Simay Demirel, Aleyna Yüce, Berna Balçık
In this context, the settlement is conceived not merely as a parcel containing residential units, but as a micro-community defined by its internal dynamics, articulated open spaces, and social focal points. Landscape operates not as a background element but as the primary organizer of the design, shaping spatial experience through squares, gardens, and pedestrian axes.
The social facility located along the main entrance axis is treated not only as a functional unit but as a threshold space that guides user experience and defines the public character of the settlement. Composed of programmatic elements such as the clubhouse, swimming pool, and yoga terrace, this structure forms a focal point that encourages social interaction and supports healthy living practices. Its positioning and spatial organization establish a strong visual and physical relationship with the landscape while also functioning as an orienting element within the overall layout.
The open space system shaped around the social facility is defined through named gathering areas such as Nefes Düzü Square, Itır Düzü Square, and Kuyu Düzü Square, reinforcing spatial memory and identity. These areas function not only as transition points but as social thresholds that enable encounters, pause, rest, and collective presence.
The open space network is conceived as an active spatial backbone that guides design decisions rather than a passive landscape surrounding the buildings. Designed for different age groups and usage scenarios, these open areas create an experiential network that supports interaction in addition to organizing circulation. Children’s playgrounds, multi-purpose sports courts, and pedestrian routes are structured as components of this continuity, establishing a balanced system between movement and pause, individual use and collective experience.
The existing greenhouse on the site, which contains endemic plant species, has been preserved, and the settlement layout has been shaped with respect to this productive landscape. In this way, the design does not impose a new order onto the land but develops in continuity with existing natural and local values. Lavender fields, small groves, stone seating elements, and defined resting pockets further create a sequence of open spaces offering experiences at different scales.
Residential units are positioned in accordance with the topography and orientation strategies to maximize daylight, natural ventilation, and views. Across different villa typologies, internal courtyards, stone-paved areas, and semi-private outdoor spaces complement the main gardens, strengthening spatial continuity. This approach defines housing not solely through enclosed interior organization, but through the relationship between indoor, semi-open, and open spaces, offering a dynamic living model.
Each unit ensures individual privacy, while the positioning of volumes and façade orientations carefully prevent direct visual intrusion between neighboring parcels. Thus, private living spaces are protected while a balanced relationship with collective life is maintained through semi-public open areas and a permeable landscape structure. Rather than sharply separating individual and communal life, the design produces a multi-layered spatial experience that defines transitions between them.
The project is not merely a physical settlement proposal, but a living model that redefines the relationship between nature, user, and space. Through spatial diversity, topography-sensitive placement strategies, and a landscape-oriented design approach, the settlement operates as a sustainable ecological and social system within itself. Within the intensity of contemporary urban life, it offers a secure and controlled framework while creating an inward-oriented world that strengthens social bonds and maintains a continuous connection with nature.
This holistic approach establishes a balanced relationship between the pace of urban life and the continuity of nature, providing users with an enriched living experience at both individual and collective scales.
Site Area: 38909,00m²
Gross Floor Area: 22255,75m²
Orçun Ersan, Sedef Yıldız, İrem Ardıç, İlginay Akyol, Hilal Delibaş, Gökçe Yıldız, Oğuzhan Çelik, Feyza Nur Şimşek, Fethi Ahmet Çelik, Feyza Nur Tekdemir, Simge Nur Topuz, Simay Demirel, Aleyna Yüce, Berna Balçık