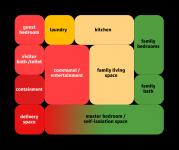
Problem Statement:
Pandemic, or globalization, is not a new problem and has existed for centuries with viruses such as plague, tuberculosis, leprosy, cholera, influenza, and so on; Since 2019, with the outbreak of the Covid-19 (Coronavirus), another round of pandemics has emerged, killing more than 5.6 million people worldwide. The first and oldest way to prevent an epidemic is to quarantine and stay home to reduce the virus transmission chain, but unfortunately the design of today's houses, apartments and complexes is not suitable for pandemic conditions, it is not hygienic and pandemic is not considered when designing. Quarantine in these shelters does not prevent the transmission of the virus as it should, but creates very difficult conditions for people in various aspects of health, social and psychological. From a health perspective, it is necessary to rethink the addition of some uses, change and modify others. From a social point of view, not anticipating safe interactive spaces in a pandemic situation, and from a psychological point of view, how to help reduce the stress of quarantine through proper housing design are some of the issues that addressed in this design. Researchers believe that after the end of the Covid-19 pandemic, the economic problems of countries will be solved sooner than the psychological problems created for the people of that country, and solving the psychological problems that arise will take much longer.
Necessity of Design:
As mentioned, houses, apartments and residential complexes estates today are not suitable for pandemic conditions and do not meet the new needs of the pandemic era, and they are called unhealthy housing in which being quarantined has many negative consequences in terms of health, social and psychological; On the other hand, the expansion of the city by villas has many negative consequences, the most important of which is the increase in air pollution by carbon dioxide and as a result of global warming and environmental issues, which according to the World Environment Organization in 2016, environmental issues Causes zoonotic diseases and the onset of pandemics; As a result, it is necessary to design a residential complex compatible with the pandemic era; On the other hand, according to researchers, Covid-19 will not be the last pandemic and we will definitely have other pandemics ahead, and the possibility of providing health certificates (compatible with the pandemic era) for buildings in the coming years is not so far off.
Design goals:
• Design of a residential complex compatible with the pandemic era.
• Review and change spaces and spatial relationships when designing to solve functional problems.
• Increasing the spatial quality of apartment units and thus encouraging people to live in residential complexes.
• A health housing complex where the health of the residents is maintained and the risk of contracting the virus is reduced.
Consideration to the following scales:
• Object scale: hygiene
• People scale: distancing and isolating
• Interior spaces: air control
• Residential: intermediate housing
• Working: telecommuting, size and dispersion
• Shopping: proximity and downscaling
• Transportation: walking, bicycling
• Higher scale: mixed use neighborhoods
Abstract:
COVID-19 has highlighted the disruptive, cross-sectorial effects a sudden-onset pan-demic has on a globally interconnected world. A particularly insidious component is the high percentage of asymptomatic cases allowing the virus to seed undetected. The design of residential architecture will need to adapt to the new reality that COVID-19 will not be the last coronavirus epidemic.This project addresses the implications for COVID-19 for new residential construction. The presence of a containment space at the beginning of the entrance to the house prevents uncontrollable external environmental threats. By separating the entertainment space, the family bedroom, the guest room and a master plus bedroom to separate the sick person, the spread of the virus is prevented. All rooms must have direct access to the outside space. The implications of this new design on existing housing stock are also discussed. The advocated concepts are novel and advance the design considerations for future residential developments.
Design process:
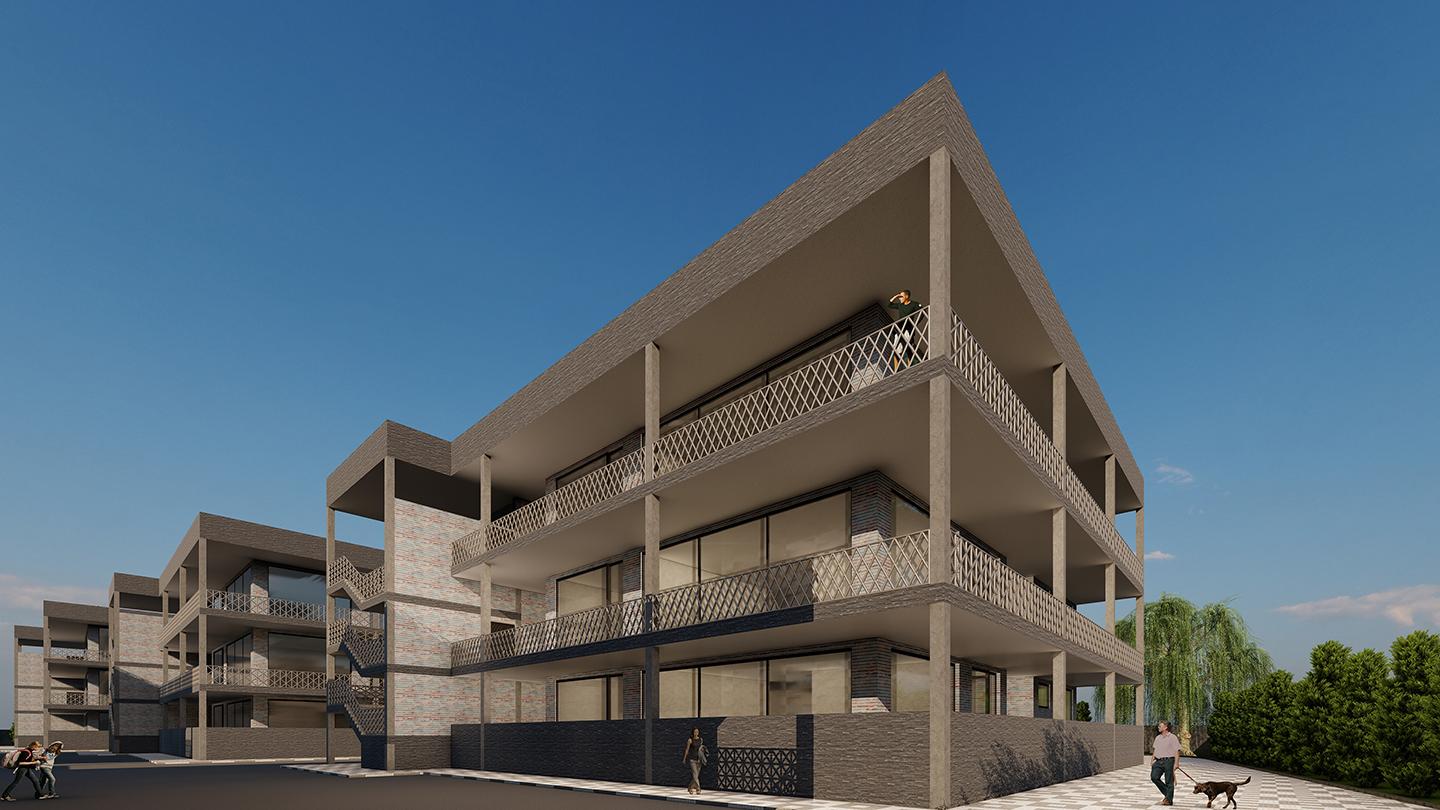
The design is based on the diagram of the spatial relations of the health house, in which a lot of attention has been paid to the safe social distance and the location and connection between the spaces of the house. Due to the fact that the residential complex must be of intermediate housing type, the number of floors in each block is 3 floors and each floor is an independent residential unit.
Vertical communication is done using two private elevators and a public stairway with going wide 3 meters to maintain social distance in the stairwell in pandemic conditions. An elevator goes only to the first floor and another elevator goes to the second floor. The elevators are completely private and can be used with a key card, so only residents who have a key card can use the elevator. The main entrance doors of each unit also open with a key card.
Because there had to be a direct connection from the rooms to the outside space, sliding windows were designed to provide a direct connection to the stairwell and elevator via the balcony. The windows are triple glazed with 10 mm smoky glass.
The main materials used in the facade are three types of refractory bricks. The reason for using a brick facade is due to its nativeness and its use in the historical monuments of Shiraz (a city in south-central Iran) and its very high durability. In the northern view, a different type of brickwork is used, which has created a beautiful effect.
In the design of the railings inspired by girih tiles, diagrid-based modeling was done, and finally railings with different and complementary details were created that show the sense of unity in geometry. The distance between the blocks in the complex is such that in the cold season of the year, by reducing the angle of sunlight, the geometric texture of the railings is imprinted on the wall of the ground floor courtyard and creates an attractive and different atmosphere. The railing is made of metal tube, which allows the virus to survive less during the pandemic and to prevent and minimize the transmission of fomite contamination.
The parking lot of the complex is open plan and there is no more of narrow and dark underground parking lots! Each parking lot is 3 by 5 meters, which consists of two walls and a sloping roof, the roof of which is a solar panel. The openness of the parking lot allows air circulation in the parking space and uses daylight to illuminate the parking lot. Each unit has two parking lots, which will have a total of 30 parking lots with a solar panel roof, which together with the solar panels on the roof of the blocks can provide a large amount of electricity required by the complex. There are 12 open parking spaces for guests.
2021
Site Location: Farhang Shahr neighborhood, Shiraz, Fars, Iran
Site Area: 12,564 m^2
Building area per each block: 733 m^2
Number of blocks: 5
Number of floors of each block: 3
Number of units per block: 3
Total number of units: 15
Roof structure: Cobiax CBCM-E-270
Mohammad Ghorbanzadeh