“There is no beauty in the finest cloth if it makes hunger and unhappiness”
- Mahatma Gandhi
In early ages, Feudal system was a way of structuring society around relationships that were derived from the holding of land in exchange for service or labor. India has its own social and economic structure that can be said as caste system, this system has created similar kind of structure and many differences in people from high and low class well as labor and other people.
Getting bound with the labor force, these people are the major human resource of our country. These people refine, redevelop and restore what is intangible. We need to be aware of these hidden but the most crucial human resources. One has to find a solution that can compensate for the loss of our significant and sole human resource.
In country of 1369 million people there are 402 million workers making it 39.1% of population. (Census India, 2001). Industrial sector has maximum no. of workers which is 42 million after agriculture sector (166 million), showing that major population of country are workers. In all these industries there are certain sectors where worker faces occupational safety and health issues. This hazardous working condition for the blue collar job is often considered as “3D” (Dirty, Dangerous and Demeaning) is performed by workers who live nearby, in village or migrant workers and yet they live from day to day situation.
These industries require massive amount of work force to keep it running, we can say that workers are back bone of these industries, most of the workers live in nearby areas who either are the migrants or from the outskirt of the city. They work at very low pay rate and do not have any secondary source of income.
Aim
To evolve an architecture solution by involving tanneries workers in design process to uplift their living and conditions based on their socio-economic situation.
2021
2021
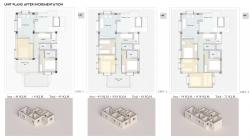
Programme includes housing , PHC and pre primary school with commercial development. House typologies are derived from affordability calculation of each people’s economic status and house hold size and option for incrementation.
Design is divided in basically four parts infrastructure, basic facilities, housing and social-economic spaces that will result in integrated habitat design. The core design idea evolves around the concept of affordability, livability, and sustainability. Possibility of increase in family member creates necessity of additional spaces within the house, therefore incrementation of spaces within the units is also considered. This additional spaces also can be modified as per the users requirement and still will can be regulated threw long term plan.
Abhishek R. Donda
Supervisor/Guide - Prof. Niraj Naik
Favorited 1 times