This project proposes a heritage interpretation centre in Rijal Alma'a, Saudi Arabia, to attract visitors and raise public awareness towards culture and heritage through modern and diverse means of communication. Rijal Alma'a is one of Saudi Arabia's unique sites that is rich in local arts and natural scenery. However, it is barely recognized by outsiders due to lack of attractions in the village.
The project offers informal educational spaces and cultural-social interaction through its seminar halls, lecture room, exhibition halls, outdoor theater, library, observation decks, and workshops of local craftsmen. The project has some supporting services as well, such as a small administration zone, a restaurant with a view over the village's main plaza, and a hotel with traditional-like chalets to boost the whole experience for long-stay visits.
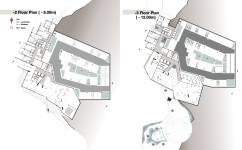
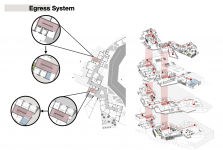
The Centre will be located on a contoured site along the Souda Mountains overlooking the main plaza of Rijal Alma’a; therefore, ideally, visitors enter from the top floor, where they are introduced to the village through the viewing decks, and as they're descending, they get deeper into the cultural journey and learn more about the past since the exhibitions are placed in the bottom floors and buried into the mountain layers to align with the concept of making the invisible visible as heritage is the hidden gem of our present. There are two main circulation paths: cultural and leisure, or educational, in addition to the separate circulation of the hotel for long-stay visitors. Visitors will cross paths; however, they will have different journeys based on their visiting purpose.
The design approach emphasizes the concept of conserving heritage; thus, the architecture of the building resembles the traditional architecture of the village—orthogonal and overlapping forms that are earth-toned—with a modern twist that is reflected by cantilevered, glass-structured viewing decks, sharp angles, and perpendicular masses.
*The project’s total area is 3,926 sqm.
2022
Structural studies:
There are two main structural systems used in the project: the flat slab system due to its relatively low cost, convenience with the design, and its span in almost all spaces except for the lecture room and the observation decks, where the cantilever vierendeel truss system is used due to its larger span that allows supporting the masses without disturbing the functions as well as allowing the decks to float.
Façade system:
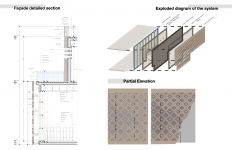
The building's eastern side is buried into the mountain; therefore, natural daylight penetration is a huge focus in the project. Thus, the chosen system for the western façades in the exhibition is glass-fin, as it allows visual continuity as well as light penetration into the interior. However, double skin is used (a GRC panel attached to the glazed wall) to act as a solar chimney and control the heat gain in the exposed walls.
Environmental Aspects:
There are multiple environmental strategies that are incorporated into the design:
1-Sustainable materials: locally sourced stone is used as a construction material for some walls to reduce the carbon footprint, and certified sustainable wood is used for the shading devices.
2-Daylighting strategies: daylighting is allowed to enter deep into the building through the use of two light wells. Also, clerestories, side openings, and double skin are used to allow light penetration throughout the whole project.
3-Passive cooling strategies: The use of greenery indoors provides evaporative cooling inside the building, while the green roofs used allow for a cooler breeze to enter the building through its openings. Outdoor greenery is also used in the southern outdoor area to create a cool breeze.
4-Shading devices: wooden shading devices are used for terraces ,and louvres are used to shade small to medium-sized openings in the envelope, while a GRC panel is used as a double skin for large openings that are most exposed to the sun.
5-Natural Ventilation Strategies: Light wells allow natural ventilation through the stack effect as well as the double skin that acts as a solar chimney.
6- Renewable energy: Renewable energy is used in the building through the application of PV panels on the southern roof. Crystalline PV panels were used, with an efficiency of 18%, and this system covers around 6.70% of the total expected annual consumption.
Student: Reem Taju
Instructor: Dr. Ahmed Waseef
Favorited 2 times