PROBLEM: increasing overpopulation in megapolises.
SOLUTION: building density maximization, providing comfort living conditions inside and outside the residential unit.
METHOD: creating a life formation, decreasing spaces between residential units.
PROBLEM1: securing daylight and insolation.
PROBLEM2: creating green spaces with playgrounds inside the life formation.
PROBLEM3: transport problem solving for the formation with increased population density.
METHOD: creating a life formation, which consists of two independent parts {ground and upper}, which would have own highway level, car park, public service establishments and common school and kindergartens.
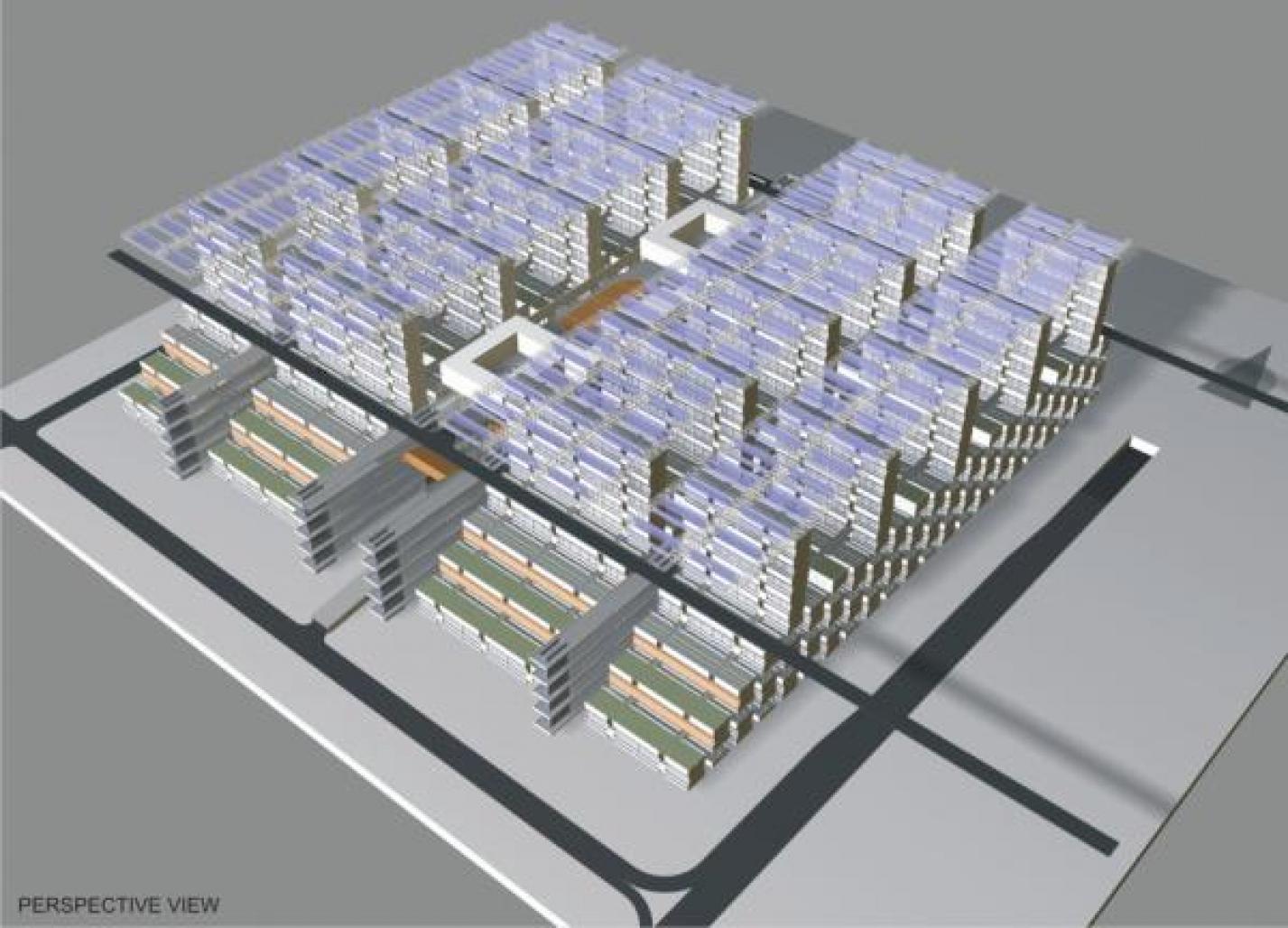
GROUND PART
Residential unit - five-storey block of flats with a gallery on the north side and quarters with south orientation.
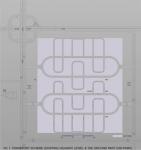
Checkered residential unit allocation would provide green-spaced pedestrian boulevard between units {see section 1-1}.
Car park locates on the level of existing highways. The ground part of the life formation should be built over the car park.
Public service establishments’ locating - see section 1-1.
UPPER PART
Projected highway level, constructed on the covering of the upper floor of the ground part, is designed in order to duplicate the existing highways - to solve the transport problem concerned with increased population. The roads could connect similar life formations, and so - cover the whole city. The projected highway level is connected with the existing ones using car ramps {see section 2-2}.
Thoroughfares’ and car parks’ location - see Pic. 2.
Green area is arranged on the covering of the car park. The playgrounds, located there, are connected with entrances to the multistorey blocks of flats with foot-bridges {see section 1-1}.
There is a truss fixed on the frame of the blocks, which provides an opportunity to arrange special mirror system for securing daylight for the ground part. See detail A and B.
SECURING DAYLIGHT AND INSOLATION
DETAIL A
System of mirrors hinged on the truss.
Ranges of discretion:
- East-West turning {180°}
-horizontal angle of inclination changing.
In that way the system forms a vertical stream of light, reflecting sun rays during all the sun day.
DETAIL B
Parts of vertical light streams are being directed horizontally, using mirrors fixed at the angle of 45. In that way we organize a stream of light 0.8x2-3.5m for each room of each flat and three streams of light for each green space. Insolation conditions are provided by running some part of the stream through glass, daylight conditions are supplied by running another part of the stream through the light diffuser.
2006
2006